Understanding the End-to-End Application
A Journey from Client to Server and Database
In the vast landscape of software development, creating an end-to-end application involves weaving together various components seamlessly. From the client-side interface to the server-side logic and the underlying database, each piece plays a crucial role in delivering a robust and functional application. In this blog, we'll explore the anatomy of an end-to-end application, highlighting the interactions between the client, server, and database, with examples in popular programming languages.
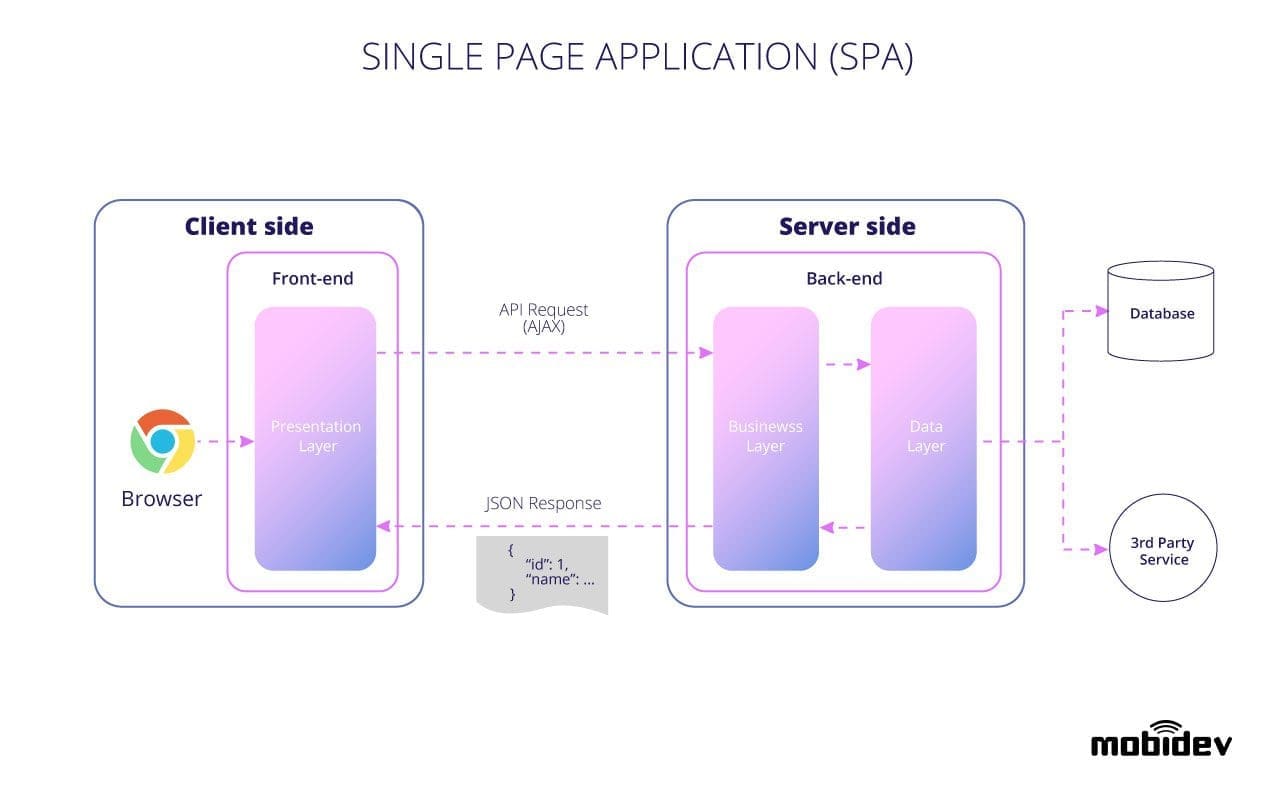
Client-Side Development: At the forefront of any application is the client-side, where users interact with the interface. This could be a web browser, mobile app, or a desktop application. Common programming languages for client-side development include:
JavaScript (Web): For web applications, JavaScript is the go-to language. It enables dynamic, interactive, and responsive user interfaces. Libraries like React, Angular, and Vue.js further enhance the development experience.
Swift/Kotlin (Mobile): Swift is used for iOS app development, while Kotlin is favored for Android. Both languages provide a native experience and seamless integration with platform-specific features.
Java/C# (Desktop): Java and C# are prominent choices for desktop applications. Java with JavaFX or C# with WPF allow developers to create rich and feature-packed desktop interfaces.
Server-Side Development: The server-side is the brain behind the scenes, handling requests from clients, processing data, and orchestrating the application's logic. Examples of server-side programming languages include:
Node.js (JavaScript): Leveraging JavaScript on the server side, Node.js is known for its non-blocking, event-driven architecture. It is particularly popular for building scalable and real-time applications.
Python (Django/Flask): Python is renowned for its readability and versatility. Django and Flask are Python frameworks that simplify server-side development, providing tools for routing, database interaction, and more.
Ruby (Ruby on Rails): Ruby on Rails emphasizes convention over configuration, streamlining the development process. It promotes the use of best practices and accelerates the creation of database-backed web applications.
Java (Spring Boot): Java, with frameworks like Spring Boot, is a robust choice for enterprise-level applications. It follows the principle of "write once, run anywhere" and is well-suited for large-scale projects.
Database Integration: Databases store and manage the application's data. Various types of databases, including relational (SQL) and non-relational (NoSQL), serve different needs. Examples of database technologies include:
MySQL/PostgreSQL (Relational): MySQL and PostgreSQL are popular relational databases known for their ACID compliance and support for complex queries. They are suitable for applications with structured data.
MongoDB (NoSQL): MongoDB is a leading NoSQL database, storing data in flexible, JSON-like documents. It is well-suited for applications with evolving or unstructured data requirements.
Redis (In-Memory): Redis is an in-memory data structure store, often used as a cache or message broker. It excels in scenarios requiring high-speed data access.
Communication between Components: The client communicates with the server through APIs (Application Programming Interfaces). RESTful and GraphQL APIs are common patterns for this interaction. Examples include:
RESTful API (Representational State Transfer): REST uses standard HTTP methods (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE) for communication. Data is typically exchanged in JSON format. Frameworks like Express (Node.js) and Flask (Python) facilitate RESTful API development.
GraphQL API: GraphQL allows clients to request precisely the data they need. It offers a more flexible and efficient alternative to REST. Apollo Server (JavaScript/Node.js) and Graphene (Python) are popular tools for implementing GraphQL APIs.
Building an end-to-end application involves orchestrating a symphony of technologies, each contributing to the overall functionality and user experience. As technology evolves, new languages, frameworks, and database solutions emerge, offering developers an ever-expanding toolkit. By understanding the roles of the client, server, and database components, developers can navigate the complexities of application development and deliver innovative and scalable solutions.
Last updated